16 Types of Plastic Processing Techniques (Part 2)
In last week’s blog post, we introduced eight plastic processing techniques. In this article, we continue with another eight methods, and we hope you find them helpful and informative.
9. Lamination Process
Lamination combines multiple layers of the same or different materials under heat and pressure into a single product. It is commonly used for plastics and rubber.
This process is similar to compression molding but allows for multi-layer structures, whereas compression molding typically works with single-material, single-structure products.

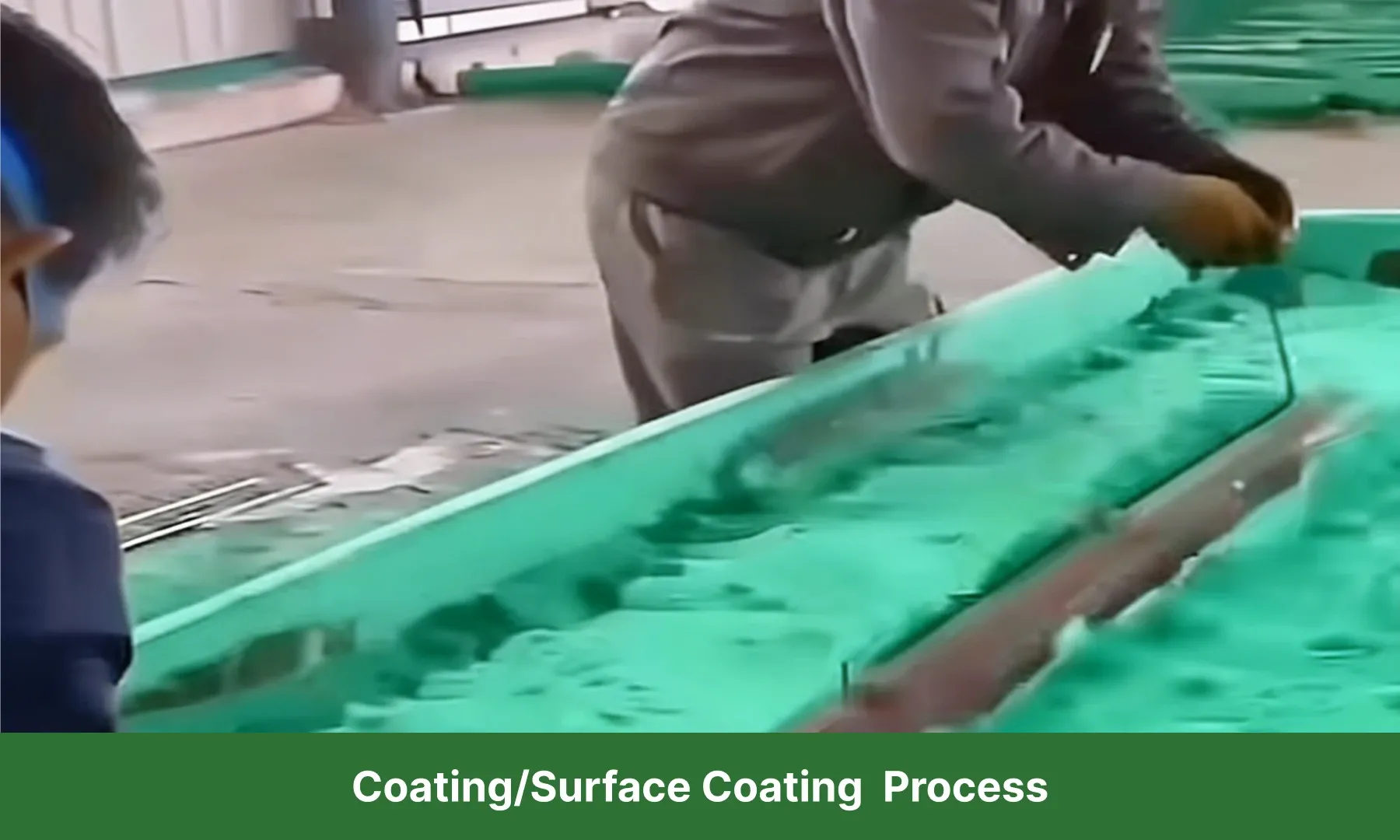
10. Coating / Surface Coating Process
The coating process applies plastic or organic solutions onto substrates such as fabric or paper to produce synthetic leather, coated fabrics, or plastic wallpapers. Powder coating on metal surfaces is also part of this process.
For example, melted resin is applied to a substrate surface, then cooled and solidified to form the desired product. This process is mainly used for large, flat plastic items.

11. Casting Process
Casting involves pouring liquid raw materials into a mold at atmospheric pressure. The material undergoes polymerization or curing to form a product that matches the mold cavity shape. Modern casting processes can also use PVC pastes or polymer melts.
Originally developed for thermosetting plastics, casting later expanded to thermoplastics. Uncured material is placed into a mold and stimulated to react and harden, similar to the square watermelon analogy used in blow molding.
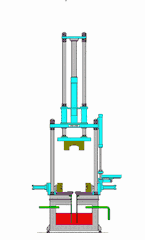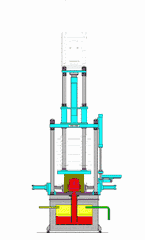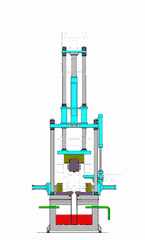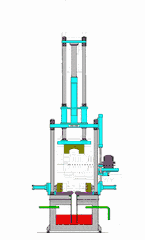
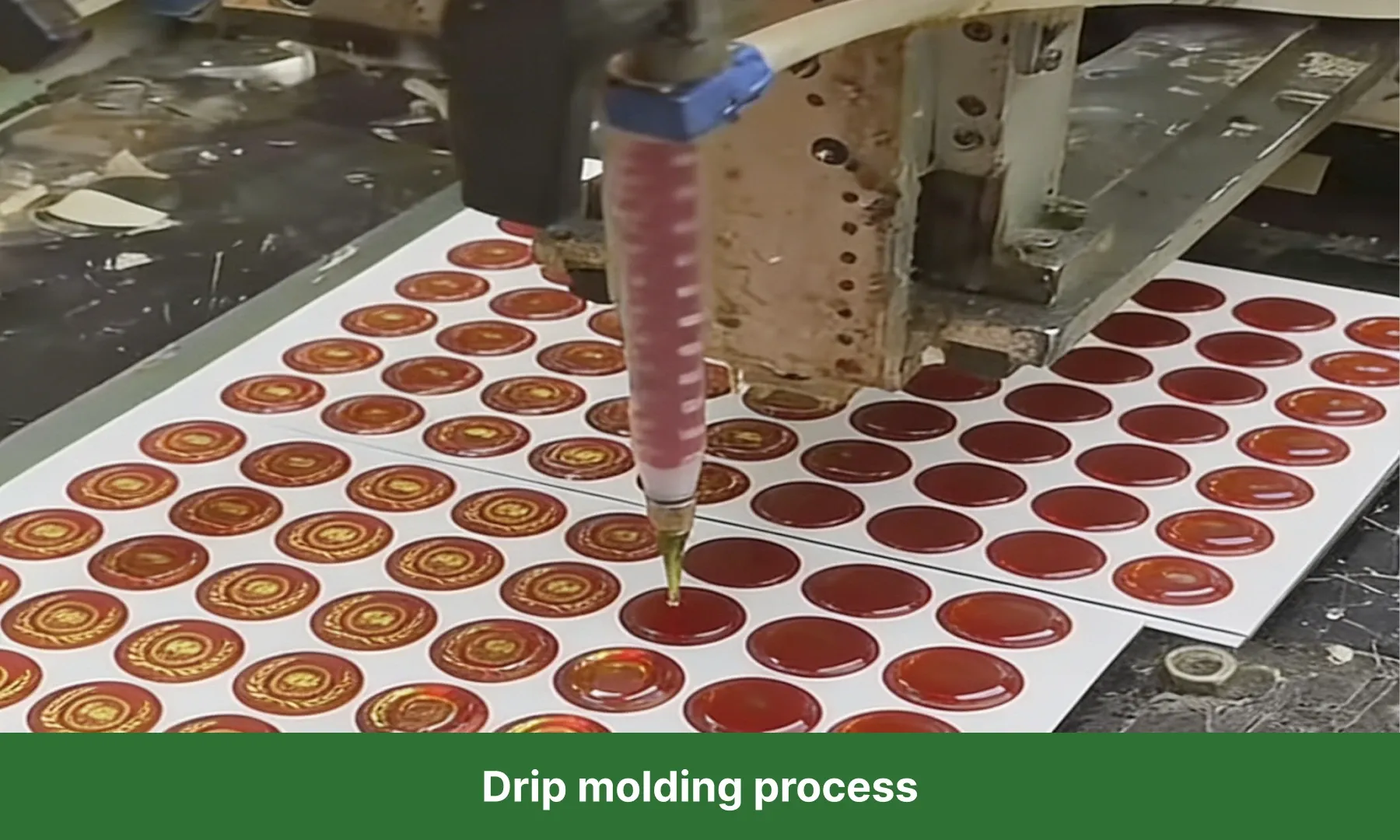
12. Drip Molding Process
This method utilizes the property of thermoplastic materials that allows them to flow when heated and solidify at room temperature. Melted material is dripped using specific tools to create shapes, then cooled to solidify.
For thermoplastic resins, this process is similar to melting wax and dripping it into molds, where it forms shapes after cooling.

13. Compression Thermoset Molding Process
This process is mainly used for thermosetting plastics. The material is heated until it melts, pressed inside a mold, cross-linked under heat, and then demolded to obtain the finished part.
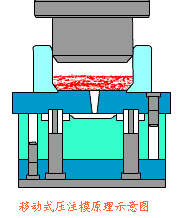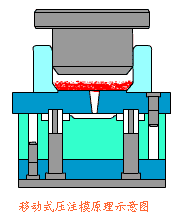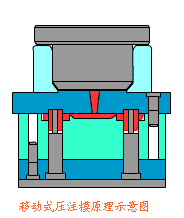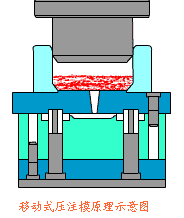
14. Extrusion Press Molding Process
Extrusion press molding is a pressure-forming method in which a punch or die compresses material inside a mold, causing plastic flow to conform to the mold cavity shape.
Even materials with low plasticity can be formed using this method. Unlike blow molding, shaping relies on mold pressure rather than compressed air.
15. Thermoforming Process
Thermoforming shapes heated thermoplastic sheets into products by softening the sheets and pressing them into molds. After cooling, trimming produces the final parts.
This process is similar to blow molding but starts with flat sheets instead of tubular preforms.
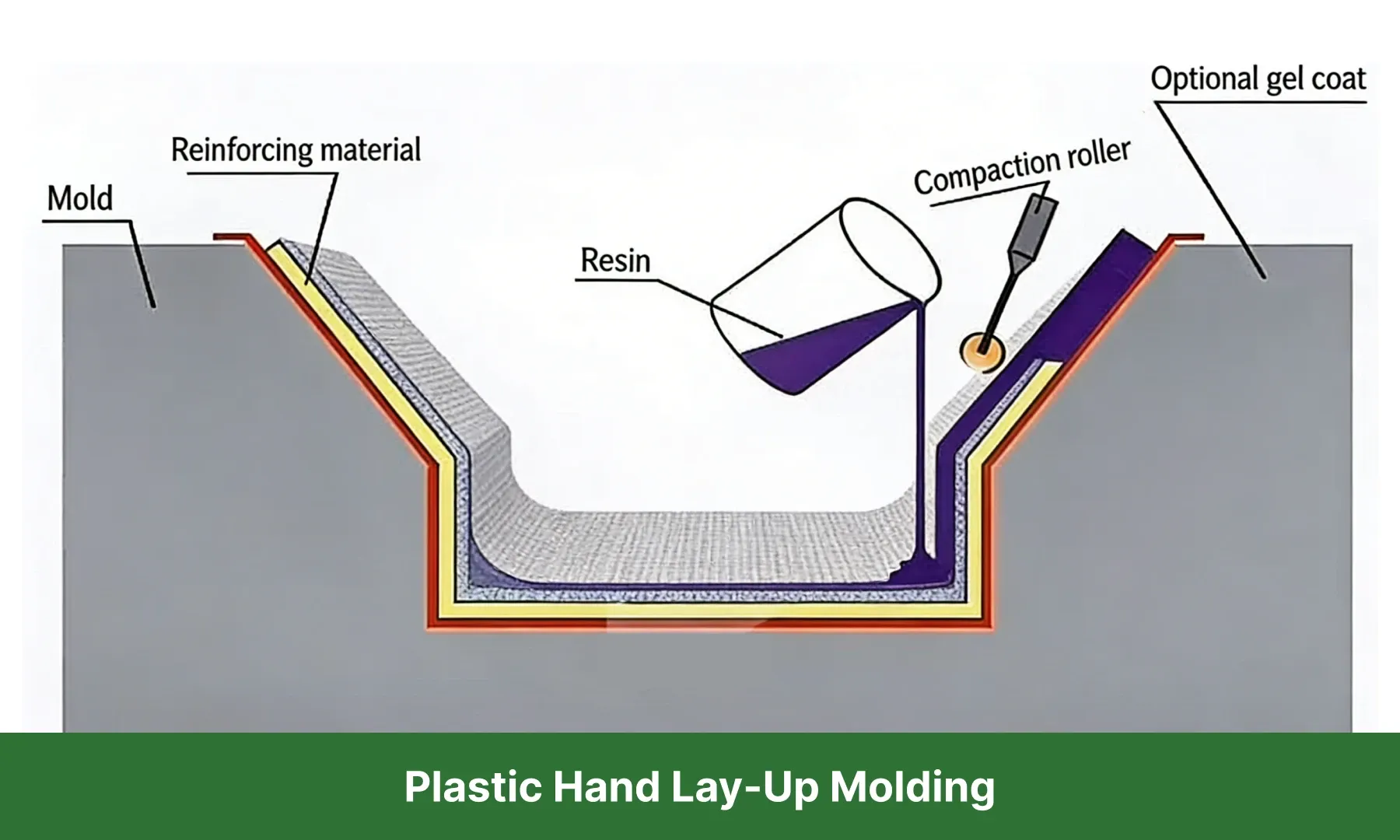
16. Hand Lay-Up Molding Process
Also known as manual lay-up or contact molding, this process involves placing reinforcement materials into a mold coated with release agent. Resin is then applied by hand until the required thickness is achieved.
After curing and demolding, the finished composite part is obtained.
Conclusion
Understanding processing methods creates value, while smooth production converts that value into output. Whether using injection molding, extrusion, or hand lay-up molding, mold sticking remains one of the largest hidden losses in production.
We understand this challenge and focus on developing efficient, environmentally friendly release agent solutions. Perfecting the process is your expertise—ensuring every mold opens smoothly is ours.






